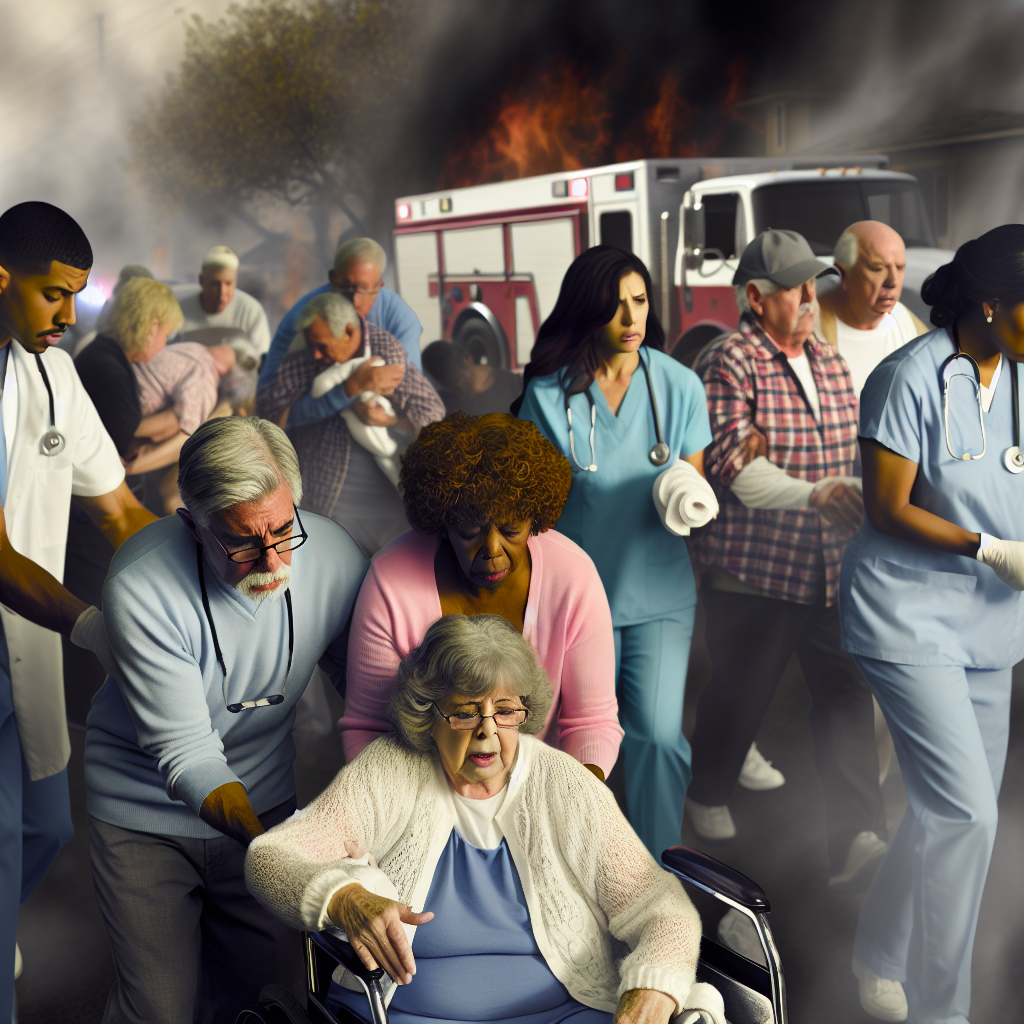
Disasters can strike without warning, transforming the lives of vulnerable populations in mere moments. Take the case of Sharlene Rabang, a 78-year-old resident who evacuated from the Maui wildfire in August 2023. After being exposed to heavy smoke during her escape, Sharlene suffered respiratory issues that ultimately contributed to her death weeks later. Her family advocated tirelessly for her recognition as a victim, highlighting the dire vulnerabilities that seniors face during disasters and the urgent need for better planning and support.
The alarming frequency of events like the California wildfires magnifies the pressing requirement for local care facilities to continually update and adhere to comprehensive disaster plans. These facilities play a pivotal role in safeguarding the well-being of seniors and individuals with disabilities, who often encounter the gravest risks during emergencies. Recent reports have spotlighted tragic instances like Sharlene’s, where assisted-living residents were left behind or inadequately supported during evacuations, illustrating the severe consequences of insufficient emergency planning and response.
The California Department of Social Services (DSS) mandates that care facilities comply with stringent emergency preparedness guidelines, yet many still falter. In this article, we will delve into the critical importance of reassessing disaster plans, ensuring that every resident is protected, and examining the tragic outcomes that can emerge when facilities neglect their duties in the face of calamity.
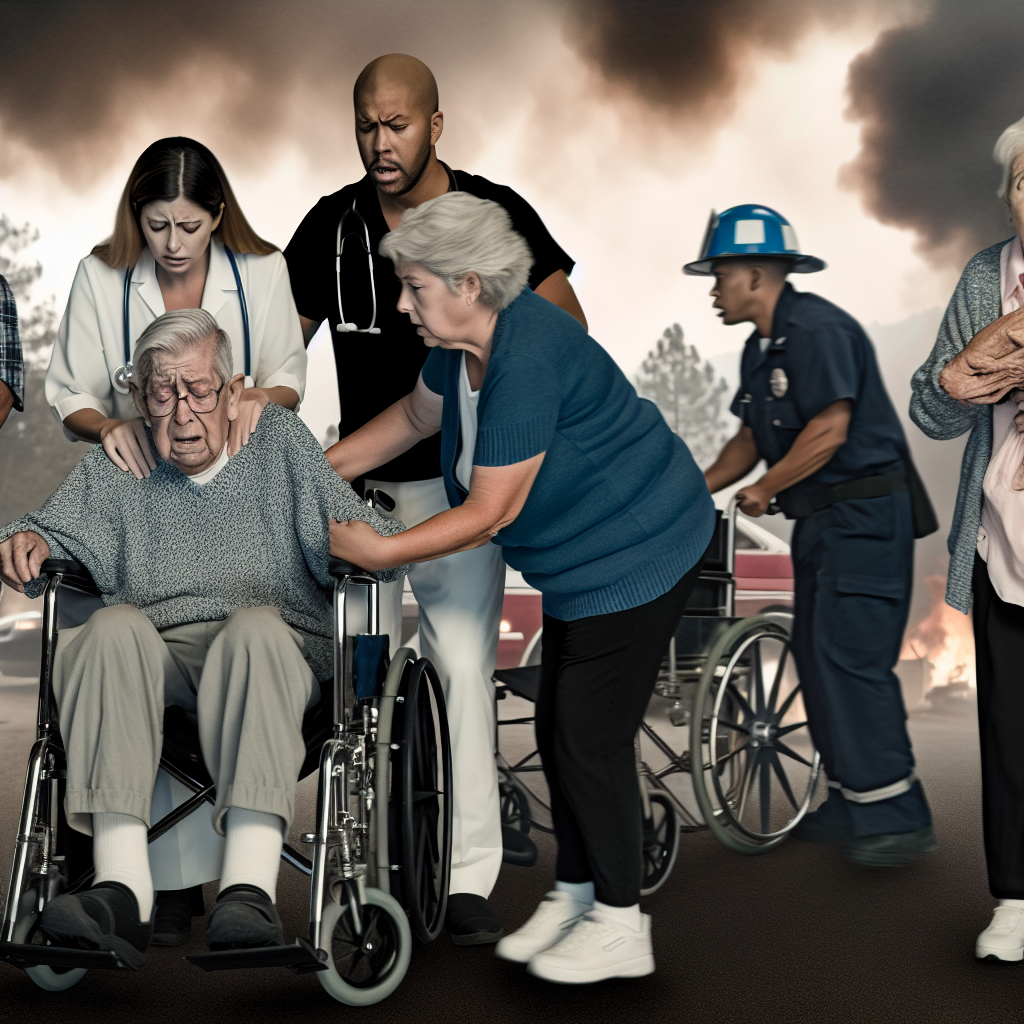

An emotional depiction of chaotic wildfire evacuation, showcasing elderly residents being assisted by caregivers amidst smoke and urgency.
DSS Mandates for Local Care Facilities
The California Department of Social Services (DSS) imposes several critical mandates on local care facilities to enhance disaster preparedness and ensure the safety of vulnerable populations during emergencies. These mandates are vital for safeguarding the health and well-being of residents, particularly in incidents such as wildfires, floods, or other disasters.
1. Evacuation Procedures
All care facilities must develop and implement comprehensive evacuation procedures. These plans should clearly outline safe exit routes and designated assembly areas. It is crucial to ensure that staff are specifically trained to assist residents, including those with mobility challenges. Regular drills should be conducted to familiarize both staff and residents with evacuation protocols. This approach ensures a swift and efficient response if the need arises.
2. Self-Reliance for 72 Hours
Care facilities are mandated to remain operational and self-sufficient for a minimum of 72 hours after an emergency. This requires having sufficient supplies of food, water, medications, and backup power solutions to cater to the needs of all residents in the event of utility failures or evacuations.
3. Transportation and Communication
Transportation arrangements must be clearly outlined to ensure accessible paths and reliable methods for evacuating residents. Facilities are also required to establish effective communication strategies tailored for various scenarios to relay important information and coordinate with emergency responders.
4. Staff Training and Drills
Regular training sessions for all staff on emergency preparedness are imperative. Specifically, facilities should conduct fire drills quarterly, involving all shifts to promote familiarity with procedures and enhance response times during crises.
5. Emergency Equipment and Supplies
Facilities are required to maintain adequate emergency equipment and supplies. This includes backup power sources, first aid kits, and any necessary mobility aids. Ensuring that these resources are easily accessible can significantly impact the safety and well-being of residents during emergencies.
By adhering to these mandates, local care facilities significantly improve their preparedness levels. This commitment contributes to a safer environment for residents during unforeseen disasters.
Investigation Findings on California Wildfire Alert Failures
Recent investigations prompted by the Eaton Fire, which occurred in January 2025, have unveiled serious deficiencies in emergency planning at California assisted living facilities, specifically MonteCedro in Altadena and The Terraces at Park Marino in Pasadena. These investigations reflect a troubling trend in which elderly residents were placed in harm’s way due to ineffective emergency protocols.
Key Findings at MonteCedro
- Evacuation Failures: On January 8, 2025, as the fire closed in, staff failed to evacuate two elderly residents, including a centenarian who was later found wandering the dark hallways with a walker. This lapse was attributed to the facility’s inadequate adherence to established evacuation procedures.
- Staff Training Deficiencies: Investigators from the California Department of Social Services (DSS) highlighted that most staff members had not received any training in emergency protocols. The facility’s executive director neglected to communicate necessary evacuation procedures to staff prior to leaving, resulting in chronic mismanagement during the crisis [Patriot LA], [L.A. Times].
- Consequences for Residents: The two residents left behind were exposed to life-threatening danger. Though rescuers eventually saved them, the needless vulnerability exhibited by the facility has led to citations for violating safety codes requiring comprehensive emergency training and protocols. This incident illustrates the dire need for facilities to improve their disaster preparedness strategies and develop effective evacuation procedures.
Findings at The Terraces at Park Marino
- Negligence During Evacuation: On January 7, 2025, the facility struggled to evacuate residents as flames approached. One resident was found alone in their room and required rescue by the Fire Department, a direct violation of safety protocols designed to protect personal rights and ensure resident evacuation [Spokesman].
- Staff Response Challenges: While the facility had conducted a mock evacuation drill just weeks prior, staff members faced overwhelming challenges on the actual day, including physically carrying residents down staircases and managing multiple needs under distress. The DSS concluded that the facility violated regulations concerning resident safety and preparedness [Park Marino].
- Immediate Risks for Residents: The oversight left vulnerable residents in peril, with serious repercussions stemming from a lack of urgency and preparedness in procedures set forth for fire emergencies. The facility has been cited, and they now must revamp their emergency plans and protocols to prevent reoccurrences. These findings emphasize the importance of enhancing emergency preparedness measures and training for staff within care facilities to mitigate risks during disasters.
These conclusions point to an urgent need for local care facilities to enhance their emergency preparation through consistent staff training, updated evacuation drills, and strict compliance with regulatory mandates to safeguard residents in times of crisis.
| Preparedness Measures | MonteCedro | The Terraces at Park Marino |
|---|---|---|
| Staff Training | Majority of staff had not trained in emergency protocols. | Staff assisted actively during evacuations. |
| Emergency Recall Procedures | Lacked an emergency recall list; key staff absent. | Staff responded to assist residents during crisis. |
| Evacuation Protocols | Two residents left behind; evacuations were delayed. | One resident left in room; others evacuated safely. |
| Evacuation Outcomes | Residents evacuated too late; at least one was endangered. | All but one resident evacuated; fire destroyed the facility. |
| DSS Citations Issued | Lapses in training and procedures led to citations. | Citation for failure to evacuate one resident. |
The Vital Role of Staff Training in Emergency Procedures
Comprehensive staff training in emergency procedures is crucial for care facilities, significantly enhancing safety and ensuring regulatory compliance while improving the overall quality of care. The recent failures reported during emergencies, particularly during the California wildfires, emphasize the dire consequences of inadequate training.
Enhancing Safety and Reducing Adverse Events
Research indicates that effective training of staff leads to marked improvements in resident safety. A study evaluating a quality improvement program in 29 care homes in the UK discovered a 1.4-point increase in safety climate scores due to enhanced staff training. It reported significant reductions in incidents like falls (p = 0.0006), severe pressure ulcers (p = 0.014), urinary tract infections (p = 0.001), and various adverse events (p = 0.0003). These findings underscore how upskilling care home staff can lead to substantial safety enhancements.
Regulatory Compliance and Preparedness
The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services emphasizes that adequately training staff is an essential element of a facility’s emergency response plan. All departments within a facility must be involved in training to foster a comprehensive understanding of emergency protocols. It should include initial training and ongoing education to ensure staff readiness for varied emergency scenarios.
Improving Knowledge, Skills, and Abilities
There is a strong correlation between enhanced staff knowledge, skills, and abilities (KSAs) and overall team effectiveness in handling emergencies. Training focused on these areas not only revitalizes staff but also keeps their skills current, positively influencing patient outcomes. Furthermore, maintaining compliance with state and federal regulations through consistent training mitigates financial risks stemming from quality assurance audits.
Addressing Training Gaps and Competency
Failing to address training gaps can expose residents to significant risks. A study in BMC Public Health highlighted the necessity of identifying and rectifying gaps in hospital staff’s knowledge concerning mass casualty incidents and disaster management. Regularly updated training, tailored to specific medical roles, is crucial to improving hospital preparedness and staff resilience, particularly in facilities with staff members who have shorter lengths of service.
The alarming events seen in care facilities during the California wildfires illustrate the critical importance of ongoing and rigorous staff training in emergency procedures. Overlooking this essential aspect of care not only places residents in jeopardy but can also lead to severe repercussions, including loss of life and legal penalties. Investing in comprehensive and continuous training is vital for care facilities to ensure that staff are effectively prepared to respond to emergencies, thereby safeguarding the welfare of their residents.

Emergency Preparedness Failures in California’s Assisted Living Facilities
In examining recent findings about emergency preparedness failures in California’s assisted living facilities, expert opinions illuminate the broader implications for community responsibilities and disaster response.
Laura Mosqueda, a renowned expert in the field, emphasized the chaotic nature of the situation that unfolded during the California wildfires. She stated,
“Absolutely it was chaotic because of the fires, and absolutely [assisted-living facilities] have a responsibility to have emergency plans and competent leadership who can follow through.”
Her remarks underscore a critical need for these facilities to not only establish but also effectively execute robust emergency plans. Mosqueda’s insight advocates for a fundamental reassessment of the operational protocols within care facilities, emphasizing that mere existence of an emergency plan is insufficient without trained personnel capable of following through during crises.
Conversely, John Ward, a stakeholder impacted by the findings, shared a more nuanced perspective. He acknowledged the mistakes made during the evacuation but insisted on recognizing the positives of the community environment where his mother resides. He remarked,
“The report confirmed that mistakes were made that night, but I can’t let it overshadow the positive community where my mom lives day-in and day-out.”
Ward’s comment reflects the importance of focusing on the overall quality of community care while also recognizing areas for improvement. His view points to a delicate balance between accountability for mistakes and appreciation for ongoing care efforts, emphasizing that the responsibility lies not just with the facilities but also with the community to advocate for heightened preparedness.
These insights reinforce the necessity for communities to actively engage in emergency preparedness discussions, urging local care facilities to bolster their resilience to protect vulnerable populations during future emergencies.
Conclusion
As disasters such as wildfires highlight the vulnerabilities of assisted living facilities, it is imperative to recognize that disaster preparedness is not a one-time effort but a continuous obligation. The findings of recent investigations accentuate the essential need for care facilities to regularly update and comply with the mandates set forth by the California Department of Social Services (DSS). Adhering to these guidelines ensures that facilities can effectively protect their residents during emergencies.
To prevent future tragedies, facilities must prioritize enhancing their disaster protocols and training programs. This involves not only developing more robust evacuation plans but also conducting regular drills and comprehensive training sessions that equip staff with the necessary skills to respond swiftly and effectively when crises arise. Facilities should foster a culture of preparedness that extends beyond regulatory compliance and focuses on the safety and security of their most vulnerable populations.
In light of these considerations, we urge all care facilities to take immediate action to revisit their disaster plans, engage in consistent staff training, and enhance their operational readiness. Together, we can work towards creating safer environments where every resident is truly protected during emergencies, ensuring that no one is left behind in times of crisis.

The following authoritative sources provide insights into disaster preparedness standards for care facilities, specifically in relation to regulatory compliance:
- Emergency Preparedness Rule – Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) – This rule mandates that facilities develop and maintain an emergency preparedness program that includes risk assessments, communication plans, and training.
- 42 CFR § 484.102 – Condition of participation: Emergency preparedness – This regulation requires Home Health Agencies (HHAs) to establish emergency preparedness programs that include emergency plans based on risk assessments.
- Emergency Preparedness Resource Center – Indiana Department of Health – This resource assists long-term care facilities in compliance with emergency preparedness regulations.
- Emergency Preparedness/Evacuation Planning for Health Care Facilities in NYS – LeadingAge New York – This outlines requirements for emergency preparedness and evacuation planning for health care facilities in New York State.
- Audits of Nursing Home Life Safety and Emergency Preparedness – Office of Inspector General, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services – This report contains findings of noncompliance with emergency preparedness requirements in nursing homes, emphasizing the need for improved oversight and training.
These sources serve as crucial references for understanding the standards and regulations governing disaster preparedness in care facilities.
Top Five Lessons Learned
- Establish Comprehensive Evacuation Procedures: Facilities must clearly outline and practice evacuation routes and procedures to ensure resident safety during emergencies.
- Prioritize Staff Training: All staff should receive regular training in emergency protocols, including how to assist residents with mobility issues, to improve response effectiveness.
- Ensure Effective Communication Plans: Facilities need robust communication strategies to keep residents informed and coordinate with emergency responders efficiently during crises.
- Maintain Adequate Preparedness Supplies: Institutions should stock necessary emergency supplies, including food, water, medications, and backup power sources, ensuring they can sustain operations for at least 72 hours post-emergency.
- Focus on Resident Safety as a Priority: The safety and well-being of residents should guide all emergency planning efforts, ensuring no one is left behind during evacuations or other crisis situations.