In the modern era, where innovative digital tools are rapidly reshaping various sectors, the fire service stands at a pivotal crossroads. With advancements ranging from real-time data analytics to streamlined communication, technology has the potential to elevate operational efficiency and enhance decision-making in high-pressure situations.
However, this transformation is not without its pitfalls. The very tools that promise to connect and inform can inadvertently create barriers to the authentic human interactions that are vital for cultivating trust and camaraderie among fire department leadership.
As we delve into the impact of technology on fire department leadership, we must critically examine both the promising advantages it brings and the lurking risks that could undermine the foundational relationships within firehouses. In an age where a text can replace a conversation, how do we ensure that technology serves as a bridge rather than a barrier in effective leadership?
User Adoption Data
Recent data reveals significant growth in technology adoption among fire departments. Over 60% of these departments have embraced digital solutions, which include software for management and operations. A noteworthy 52% have integrated real-time data platforms. These enhancements improve situational awareness and decision-making processes during emergencies.
Moreover, cloud-based systems have seen adoption rates above 65%. This trend clearly demonstrates a move towards leveraging technology for increased operational efficiency.
Despite these advancements, challenges remain. Cultural barriers and usability issues often slow the effective integration of these tools. This underscores the need for a shift in mindset and training to maximize their potential.
As the market for fire department technology is projected to expand significantly—reaching USD 3.56 billion by 2033—the emphasis on analytics and mobile platforms promises further enhancements in efficiency and response times. This evolution is set to transform fire service operations significantly.
Benefits of Technology in Rescue Leadership
The integration of technology into rescue leadership has ushered in a transformative era in fire services, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities. Key advancements include the use of Self-Contained Breathing Apparatus (SCBA), integrated communication systems, and tablet-based reporting, each contributing significantly to better outcomes during rescue operations.
Enhanced Safety and Accountability with SCBA
Modern SCBA units are equipped with features like integrated PASS (Personal Alert Safety System) devices and telemetry systems that provide real-time monitoring of vital signs and air quality. These advancements not only improve firefighter safety but also enhance accountability. For instance, telemetry in SCBA can reduce the decision-making time during low-visibility scenarios by 30-40%, allowing incident commanders to make quicker, more informed decisions regarding rescues and evacuations. This timely data is crucial in ensuring the safety of personnel and civilians alike (Fire Engineering).
Improved Communication
The development of integrated voice communication systems has greatly improved how fire teams interact during emergencies. Next-generation radios that connect directly to SCBA masks increase clarity and intelligibility, particularly under challenging conditions. Testing has shown that speech intelligibility can rise from 60-70% to over 95% with these systems, enhancing situational awareness and reducing misinformation (NFPA Journal). Such improvements promote better command and control at the incident scene, leading to synergetic efforts among team members.
Streamlined Incident Reporting
Tablet-based reporting platforms have revolutionized how fire departments document events and analyze data. With the ability to sync real-time information, firefighters can complete reports 40-60% faster, ensuring timely data submission and compliance with standards like NFIRS. This efficiency enables incident commanders to access crucial information such as pre-plan drawings and hydrant locations instantaneously, thus optimizing resource allocation and strategic decision-making during active operations (IAFC).
In conclusion, while the incorporation of technology in rescue operations presents challenges, the positive impacts are profound. Tools like SCBA, enhanced communication systems, and effective incident reporting contribute to increased safety, quicker decision-making, and improved leadership effectiveness in fire services. As these technologies continue to evolve, they hold the potential to further streamline operations and enhance the overall effectiveness of rescue leadership.
Benefits of Technology in Rescue Leadership
The integration of technology into rescue leadership has ushered in a transformative era in fire services, enhancing operational efficiency and decision-making capabilities. Key advancements include:
- Enhanced Safety and Accountability with SCBA: Modern SCBA units are equipped with features like integrated PASS (Personal Alert Safety System) devices and telemetry systems that provide real-time monitoring of vital signs and air quality. These advancements improve firefighter safety and enhance accountability.
- Improved Communication: The development of integrated voice communication systems has greatly improved how fire teams interact during emergencies. Next-generation radios increase clarity and intelligibility, thus promoting better command and control at the incident scene, leading to synergetic efforts among team members.
- Streamlined Incident Reporting: Tablet-based reporting platforms have revolutionized how fire departments document events and analyze data, ensuring timely data submission and compliance with standards.
In conclusion, the incorporation of technology in rescue operations presents challenges, but the positive impacts such as enhanced safety, quicker decision-making, and improved leadership effectiveness in fire services are profound. Technologies like SCBA and effective communication systems hold the potential to further streamline operations and enhance the overall effectiveness of rescue leadership.


Challenges of Technology in Fire Service Leadership
While technology brings numerous advantages to fire service operations, its rapid adoption also presents significant challenges that leaders must navigate. One of the most pressing concerns is the reduction in face-to-face communication. As digital tools become more prevalent, there is a tendency for teams to rely heavily on text messages and emails, which can lead to misunderstandings and a lack of emotional connection. This erosion of direct, personal communication diminishes the depth of relationships among fire service personnel, making it harder to build the trust essential for effective teamwork.
Additionally, the reliance on technology can create trust issues, especially when team members feel that critical information might be omitted or misinterpreted through digital channels. Leaders must foster an environment where open communication is encouraged, urging team members to share thoughts and concerns candidly, rather than retreating to electronic methods of interaction. This can often feel more comfortable, but in high-stress situations inherent to fire service operations, genuine connections are crucial.
Finally, tech-driven environments can inadvertently lead to a culture where employees feel less accountable to one another, impacting morale and collaboration. It is vital for fire service leaders to recognize these challenges and strategize ways to balance technology use with the human elements of leadership that are so foundational to effective operations.
Quotes from Industry Experts on Technology’s Influence in Fire Departments
As the landscape of fire service communications shifts with advancing technologies, insights from leaders in the field provide a critical perspective on these changes. Division Chief David Farnum emphasizes the need for thoughtful communication amidst this digital transformation:
“With the ability to reach people instantly, careful and considerate communication remains a hallmark of effective leadership and decision-making because the fundamentals of connection and leadership remain the same: Real dialogue and meaningful engagement are the ultimate opportunities for understanding and progress.”
He also notes,
“In the fire service, much of our communication is operational—radio traffic filled with quick back-and-forth confirmation of orders resulting in effective tactical coordination. But leadership in non-operational settings goes beyond efficiency; it requires understanding the preferred communication styles of team members and fostering genuine dialogue.”
This view is reinforced by Eddie Buchanan, who stresses the importance of maintaining human connections even with modern tools:
“That is where most of our work should continue to focus: using all the tools at hand to communicate information consistently, while ensuring that we maintain a human connection. Intentionality of communication and understanding messaging must become an overriding part of the education and development that fire service leaders receive moving forward.”
These insights highlight the complex relationship between technology and the leadership dynamics within fire departments, urging a balanced approach that values both efficiency and human connection.
| Aspect | Traditional Leadership Approaches | Technology-Driven Leadership Approaches |
|---|---|---|
| Communication | Primarily face-to-face discussions and direct interaction | Utilizes digital tools like messaging apps and emails |
| Decision-Making | Often relies on experience and intuition | Data-driven decisions supported by real-time analytics |
| Team Cohesion | Builds relationships through personal connections | Risk of disconnect due to reliance on technology |
| Training and Learning | Hands-on training and in-field experience | Online training and simulation tools |
| Accountability | Direct, personal accountability among team members | Digital tracking and reporting leading to potential detachment |
| Crisis Management | Immediate, on-site assessments and personal judgement | Analysis of data before and during incidents |
| Relationship Building | Emphasis on trust and camaraderie through interactions | Risk of reduced personal connection due to technology use |
| Adaptability | Slower to adapt due to hierarchical structures | Quicker adaptation using new technological solutions |
Conclusion
To sum up, using technology in rescue leadership has changed operations significantly. These tools help improve efficiency, safety, and decision-making. Devices like advanced SCBA systems and better communication technologies allow firefighters to perform better in tough situations, which improves results during critical incidents. However, this growth in technology also brings challenges that we must not ignore.
The move towards digital communication reduces in-person interactions, which can weaken the trust and teamwork that are key to successful operations. As leaders face these challenges, the need to embrace technology while fostering human connections is clear. Finding the right balance will make operations run more smoothly and keep important leadership qualities like connection, understanding, and teamwork at the heart of rescue missions.
Communication Impacts on Team Dynamics in Fire Service
Effective communication forms the backbone of team dynamics in the fire service. As various modes of communication evolve, particularly with advancements in technology, understanding the implications of virtual versus face-to-face interactions is essential. Here are key insights drawn from recent research that illustrate the impact of these communication styles:
-
Trust and Cohesion
Face-to-face interactions inherently foster higher levels of trust and social cohesion among team members. In contrast, virtual teams often grapple with lower intra-team trust and diminished social bonds. This connection is vital in high-pressure environments like firefighting, where trust can significantly influence performance and safety.
-
Communication Dynamics
Virtual communication methods typically inhibit spontaneous discussions and informal exchanges that are common in direct interactions. The absence of these informal dialogues can lead to misunderstandings and obscure critical task awareness. In person, communication tends to be richer and more immediate, promoting clearer understanding and better team connections.
-
Performance and Decision-Making
Research has indicated a strong positive correlation between effective communication in virtual teams and job performance. Nevertheless, the efficiency gained in digital communication requires careful management to mirror the effectiveness of face-to-face interactions.
-
Management Implications
To leverage technology effectively, fire service leaders must balance operational needs with the importance of human connection. Strategies may include promoting informal interactions and prioritizing regular face-to-face meetings, even in a tech-driven environment.
-
Real-World Applications
In emergency situations, the necessity for clear and trustworthy communication cannot be overstated. Fire departments should prioritize establishing trust and camaraderie through regular in-person engagements, ensuring that technology complements rather than replaces these essential human elements.
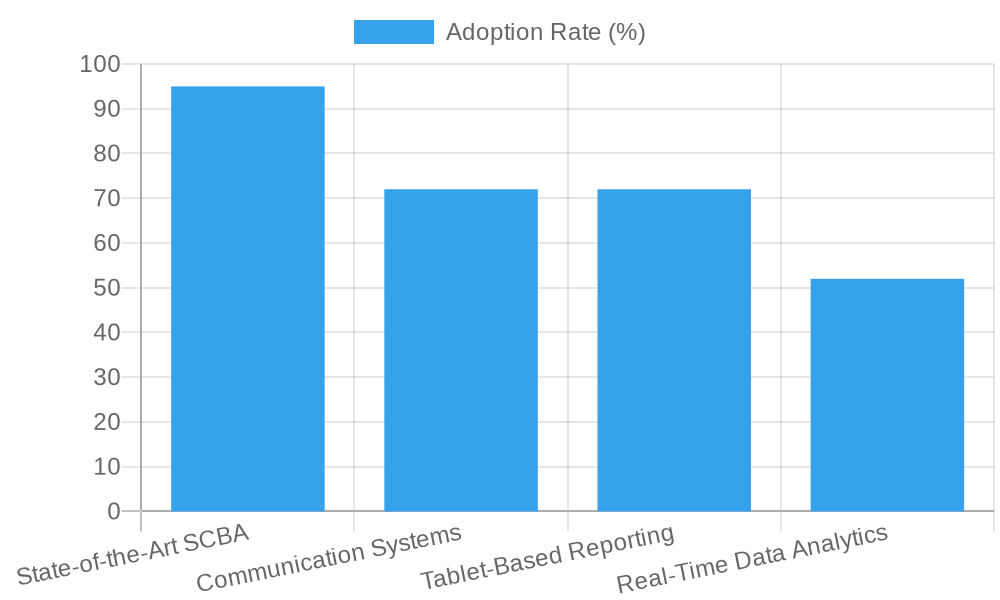
This bar graph illustrates the following technology adoption rates in US fire departments for the year 2024:
- State-of-the-Art SCBA: 95% adoption rate
- Communication Systems: 72% adoption rate
- Tablet-Based Reporting: 72% adoption rate
- Real-Time Data Analytics: 52% adoption rate
Sources:
- SCBA: Grand View Research
- Communication Systems: 360 Research Reports
- Tablet-Based Reporting: Global Growth Insights
- Real-Time Data Analytics: Global Growth Insights